Having a leopard in the neighborhood may seem a terrifying prospect, but the reality is that large predator may save your life.
A new study published in the journal Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment suggests that leopards in Mumbai, the world’s sixth most-populated city, may save human lives by feeding on feral dogs. Feral dogs are a major health issue in India, where they are the leading cause of rabies deaths.
The study was led by researchers from the University of Queensland School of Earth and Environmental Sciences.
Sanjay Gandhi National Park, with a population of 35 leopards, has the densest population of these big cats in the world. The park is also in the middle of the burgeoning city of Mumbai, with more than 20 million people. Approximately 350,000 people, many of them in poverty, live all along the periphery of the small national park. Leopards can be seen strolling the city streets, and hunting in parking garages.
“While leopards are often in conflict with people over livestock like cattle and sheep and are frequently persecuted throughout their range, we show that these unique predators can also be beneficial to human society,” says Christopher O’Bryan, one of the joint lead authors on the study, and a PhD student at the University of Queensland.
That’s because 40 percent of the average leopard’s diet consists of feral or stray dogs, the researchers found. The density of feral dogs in and around the national park is an average of 17 dogs per square kilometer compared to other parts of Mumbai away from the park boundary that can have upwards of 680 dogs per square kilometer.
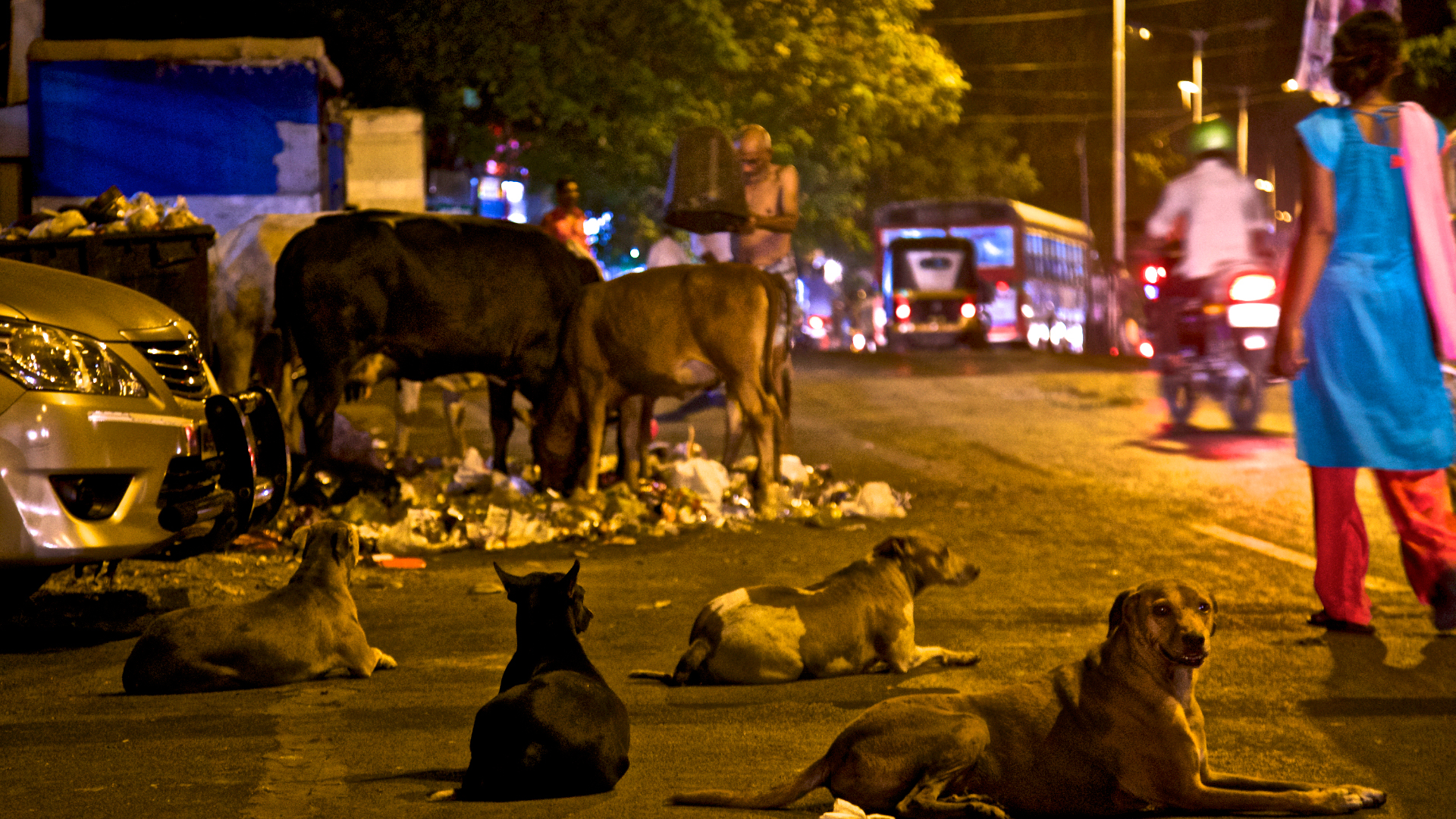

India’s rising feral dog population causes a major health crisis in the country. While exact population figures are difficult to verify, many sources estimate 30 million stray dogs live in India. Approximately 20,000 people per year die of rabies, most of them due to dog bites.
The study found that the small population of leopards “may consume about 1,500 dogs per year, saving around 1,000 bite incidents and 90 potential rabies cases.” The presence of leopards was also estimated to save $18,000 in dog management costs.
“Dog bites in these slums are very costly to people,” O’Bryan told me in a Skype interview. “There are the costs for medical treatments and hospitalization, as well as the costs associated with lost work time.”
O’Bryan is quick to point out that living with leopards has its own risks and costs. In 2017, there were seven leopard attacks in the area. “A lot of the news coverage focuses solely on the negatives of the leopards,” says O’Bryan. “The leopards can certainly be a health hazard. We are suggesting that they may also be a health benefit. We believe it’s important to assess both the costs and benefits associated with living in close proximity to predators.”
This study is a notable departure from usual studies on the benefits of large carnivores, which usually focus on predator effects in large national parks and protected areas. The classic example is research on the ecological benefits of wolves in Yellowstone National Park, which has shown that reintroducing these predators has had a host of cascading effects, including causing changes in elk behavior that leads to revegetation of native plants along streams.
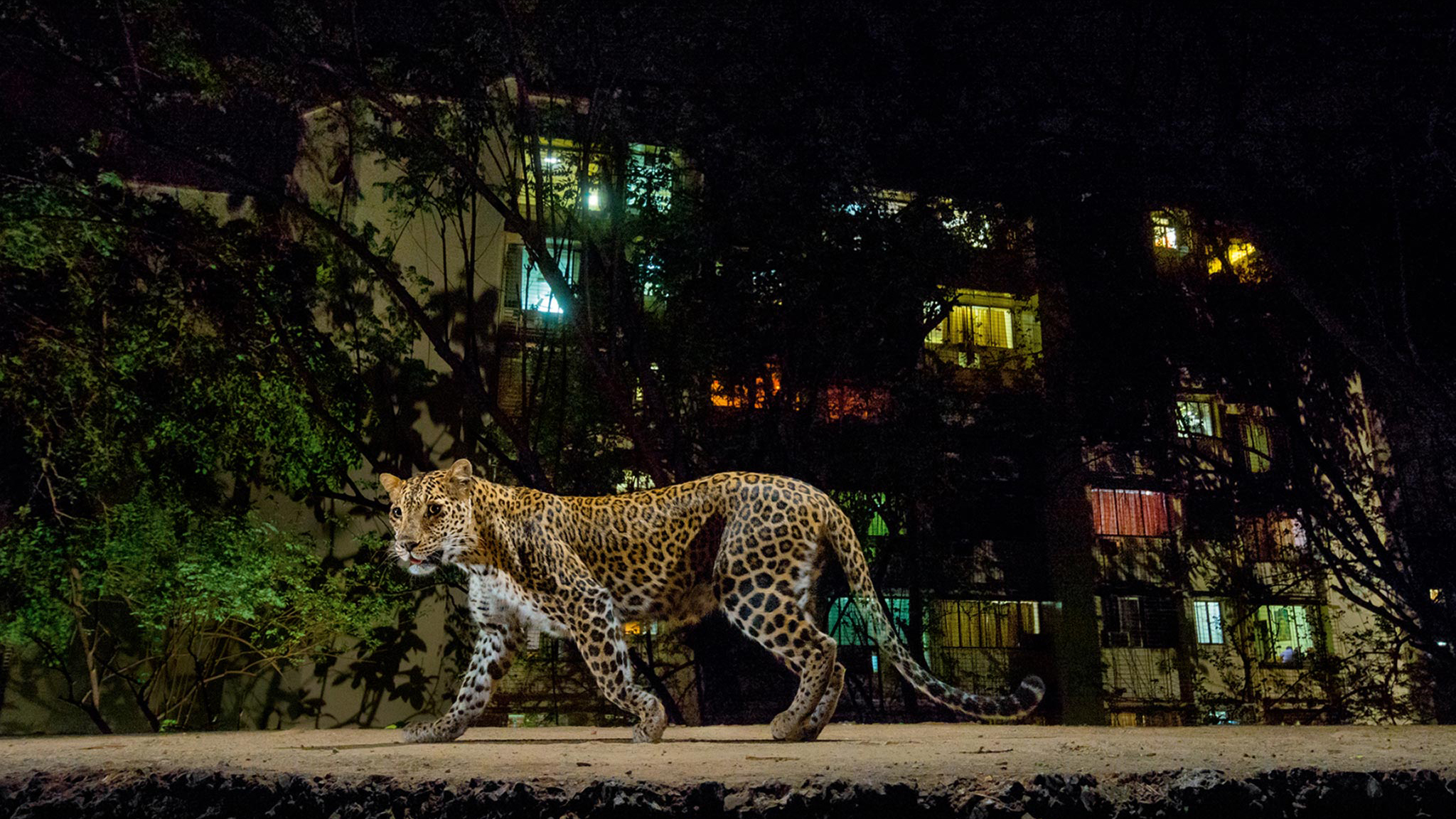
That study, and others like it, focus on the benefits to the park’s ecosystem. “This leopard study may be the first research that looks at a large predator’s effect on human health and well-being,” O’Bryan says.
Around the globe, expanding human populations encroach on predator habitat. This is often portrayed solely in terms of conflict. Many predators are forced to adapt to what is essentially a new ecosystem. Instead of preying on just native Indian mammal species, the urban leopards hunt feral dogs.
Leopards are widespread and adaptable, but they have disappeared from nearly 80 percent of their global historic distribution. They remain in conflict with people in much of their range. Understanding their benefits to people – and the benefits provided by other predator and scavenger species – may help shape a future where people and predators can better coexist.
“There are so many questions that arise from this study, and that’s a good thing,” says O’Bryan. “We see this as a call for more research on the costs and benefits of predators in human-dominated landscapes.”
The article Leopards provide public health benefits in Mumbai, India appears in the March 2018 edition of Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment journal.
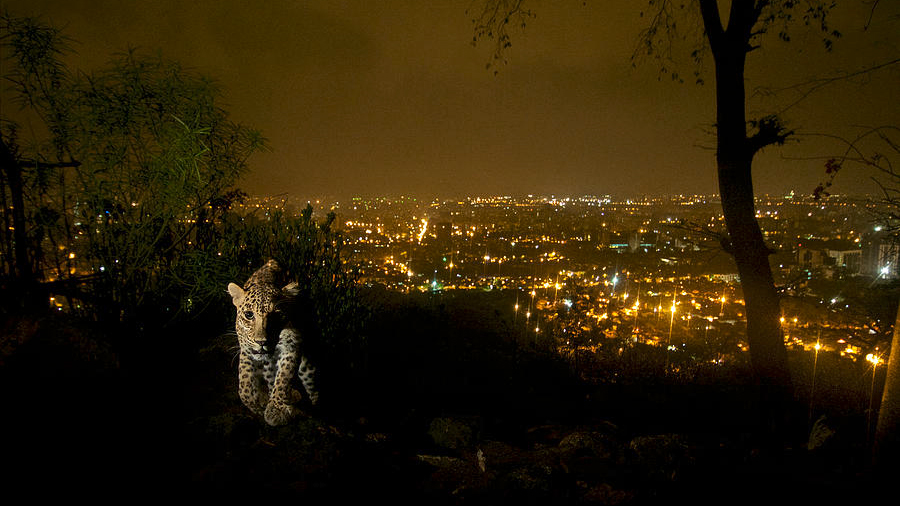




Mumbai leopards preying on ferril dogs has half a chance of helping the local people solve a devastating public health problem. Ninety cases of rabies a year is unacceptable and, uncurable. If Western cultures impose their/our “dog values” on Mumbai, the citizens of Mumbai don’t stand a chance. Here is an issue where doing nothing (about the leopards), could be the best solution. Bringing attention in the Media to the dog/leopard relationship is fraught with hazards.
However, local outreach to affected areas would keep a low profile and conceivably be more effective in protecting these communities from both rabies and leopard bites.
A large government program to capture and destroy dogs or vaccinate them is not going to happen. Besides the concept is disgusting. Poisoning, trapping, shooting and all of those traditional solutions benefits no one. We have been there done that.
Obviously not that many feral dogs can have rabies or some leopards would get. 20,000 people a year die from rabies in India (but not all from feral dogs bites,) then from where? India is on the horizon to have fresh water problems, I recently read in a Nat Geo article on the diminished U.S. Ogallala aquifier. Also read India’s human population will soon surpass China’s 1.4 billion & continue vastly increasing during this century. Spaying & neutering dogs as someone suggested, would solve dog problem but costs money & is not being done. And would not solve India’s more pressing ‘real’ problem. Several years ago India began an effort to ‘sterilize’ women in their worst overcrowded, poorest areas. The world brouhaha that started was greater than when China embarked on their one child per family policy. It may be that the human species remains blinded by continued articles re over-concentration on animal population control.
Are Big Cats or just specifically Leopards or is it even more environmentally specific to an area that Big Cats are able to build up a tolerance/immunity to certain illnesses specific to the said area; in this case, rabies virus, parvo, distemper, along with other viruses and “bugs” (that we in the U.S.A. & other areas I presume, would take our puppies & then later, the yearly visits to the vet to keep our dogs current on their vaccines so they do not get sick, get our children, other animals or ourselves sick!! Just as we vaccinate our children, to keep them safe, we need to keep our animals {in my case, MY ANIMALS ARE MY CHILDREN & ARE TREATED AS SUCH!!!!!} SAFE!!!!! We NEED TO keep them safe every day, in every way that we can, PERIOD!!!!!)
As Bob Barker said for so many years: “HELP CONTROL THE PET POPULATION, HAVE YOUR PET SPAYED OR NEUTERED!!!!!” I say, keep track of your Babies 24/7/365!!!!! I know EXACTLY where mine are all the time! When they are outside, I am also!
I just hate seeing animals – ANY ANIMALS – being harmed!!! If one needs to feed their family, fine do what you have to do as humanely as possible & use as much of that creature as you possibly can so that there is no waste of life!!
Thank you to everyone that loves & cares about animals as much as I care – you are special people!!!!!
Thank you in advance for answering my questions!! And thank you for the interesting article!!!!!
Cathy ?
If leopard ate a rabid dog wouldn’t it get rabies also? Just wondering.
Hi Constance,
It’s a good question. While leopards in Mumbai have not been documented to have rabies, there have been cases elsewhere of leopards having rabies.
Regards,
Chris O’Bryan
Really interesting.Plays on my senses…protect leopards, definitely, feel sorry for the dogs. Must realized that it is a different world over there. Must read the blog, I have been trying all of my life to make sense of it all. I tried to get into that field of work but years ago it wasn,t possible…So much to learn, and I believe we all need to share and understand. Thank you.
I am ignorant to the full scope of information on rabies; so please enlighten me. Would the rabies-infected dogs therefore also infect the leopard? Thank you for your time.
This is horrific these poord ogs they need to have someone help them. This is not ok we people to vaccinate them and find them homes
What’s keeping a leopard from eating human beings?
If feral dogs constitute 40% of the leopards’ diet, what is the other 60%? And what keeps the leopard population in check? Do the leopards also help control the rodent population? How about snakes?
Hi Nancy,
Leopards feed on small mammals, primates, reptiles, herbivores, and even domestic buffalo. They are one of the most adaptable large carnivores in the world, consuming over 100 different prey types and living across 100 degrees of longitude.
Best,
Chris O’Bryan
The feral dog population needs to be controlled by human sources, as well…..
I have lived in Hyderabad and walked the roads at night but have never seen leopards. But the farmer who hosted me apparently has seen leopards and warned me about them.
THAT IS THE MOST DISGUSTING ARTICLE I HAVE READ IN A LONG TIME……………MUMBAI GOVT NEEDS TO SPAY/NEUTER TO STOP FERAL PUPPIES BEING BORN…………THERE ARE A MULTITUDE OF VETS FROM THE UNITED STATES THAT GO AND DO THIS ALL OVER THE WORLD………AND SUPPORT DOG SANCTUARIES AND GET FERAL DOGS OFF THE STREETS………..THIS IS 2018…………GOOD GOD ALMIGHTY………
BUT TO HAVE THEM EATEN AND SCREAMING IN PAIN FROM BEING KILLED IS ABSOLUTELY
INSANE AND INHUMANE…
I AM SENDING THIS ARTICLE TO ONE OF THE ANIMAL SANCTUARIES I SUPPORT IN INDIA…..
OMG
HI Matthew,
Thank you for the article and the interesting information. Yet another example of how every species is an essential link in the balance between all of us, even when their environment changes (usually due to us) and they are in new settings.
One question kept occurring to me while reading your article. How do the leopards NOT get rabies after eating a rabid dog?
Thanks for your answer,
Sydney
Hi Sydney,
Although it has not been documented in Mumbai, leopards can contract rabies. There are some instances where leopards have had to be rehabilitated (and in some instances died) from rabies exposure elsewhere in the world.
Regards,
Chris O’Bryan
It sounds like the greater problem is lack of birth control for humans and their dogs.
Yes, how the feral dog population, got so out of hand, is not the responsibility of leopards to solve. India needs to find a humane way, to have these feral dogs spayed, neutered, and transferred to places where they are off the streets. The pictures of them foraging are disgusting. There are many humans, who would help, from all over the world…….Start doing something!!!!
Are the cats at risk from getting rabies, since they may eat rabid dogs?
Hi Nancy, Chris O’Bryan reports that there are no instances of leopards contracting rabies from feral dogs in Mumbai the scientific literature. There are reports of leopards contracting rabies from dogs elsewhere in the world. Thank you for the question!